OBD:TXMP: Difference between revisions
(seems like we should note that ARGB8888 was inserted as a new format) |
(first brain dump of many; hopefully useful) |
||
| Line 28: | Line 28: | ||
{{OBDtr| 0x8C | int16 |C8FFC8| 80 00 | 128 | width of the image in pixels }} | {{OBDtr| 0x8C | int16 |C8FFC8| 80 00 | 128 | width of the image in pixels }} | ||
{{OBDtr| 0x8E | int16 |C8FFC8| 80 00 | 128 | height of the image in pixels }} | {{OBDtr| 0x8E | int16 |C8FFC8| 80 00 | 128 | height of the image in pixels }} | ||
{{OBDtr| 0x90 | int32 |C8FFFF| 01 00 00 00 | 1 | texture format RGB555; | {{OBDtr| 0x90 | int32 |C8FFFF| 01 00 00 00 | 1 | texture format #1 (RGB555); see below for list of available formats. | ||
:0 - ARGB4444, 16 bits/pixel, 4 | :0 - ARGB4444, 16 bits/pixel (stored as a little-Endian int16, swaps to big Endian at runtime on Mac) | ||
:1 - RGB555, 16 bits/pixel, 5 | ::Four 4-bit channels, with bitmasks 0x000F (Blue), 0x00F0 (Green), 0x0F00 (Red) and 0xF000 (Alpha). | ||
:2 - | :1 - RGB555, 16 bits/pixel (stored as a little-Endian int16, swaps to big Endian at runtime on Mac) | ||
:( | ::Three 5-bit channels, with bitmasks 0x001F (Blue), 0x03E0 (Green) and 0x7C00 (Red). | ||
:8 - RGB888, 32 bits/pixel, 8 | :::N.B. The high bit (0x8000) is unused, but the convention is to always set it to 1. | ||
:9 - S3TC/DXT1, compressed 4 times (GL_COMPRESSED_RGB_S3TC_DXT1_EXT OpenGL texture format) }} | :2 - ARGB1555, 16 bits/pixel (stored as a little-Endian int16, swaps to big Endian at runtime on Mac) | ||
::Three 5-bit channels with bitmasks 0x001F (Blue), 0x03E0 (Green) and 0x7C00 (Red), 1-bit alpha (0x8000). | |||
:3 (never used in Vanilla TXMPs) - I8, 8 bits/pixel, stored as a single byte. Monochrome "intensity" (256 levels of gray). | |||
:4 (never used in Vanilla TXMPs) - I1, 8 pixels/byte. Pixel rows, bottom to top. Monochrome "intensity" (black-or-white). | |||
:5 (never used in Vanilla TXMPs) - A8, 8 bits/pixel, stored as a single byte. Standalone alpha (256 levels of opacity). | |||
:6 (never used in Vanilla TXMPs) - A4I4, 8 bits/pixel, stored as a single byte. Intensity (bit mask 0x0F), alpha (0xF0). | |||
:7 (never used in Vanilla TXMPs<ref>Storage format 7 was jointly used by OniSplit, Daodan DLL and the Intel Mac build to allow for 32-bit textures with transparency - most importantly experimental lightmaps, see [[Lightmapping_levels|HERE]]. However, the actual storage format used in this case was RGBA_Bytes (type 11), and type 7 was used by mistake.</ref>) - ARGB8888, 32 bits/pixel (stored as a little-Endian int32, swaps to big Endian at runtime on Mac) | |||
::Four 8-bit channels, with bitmasks 0x000000FF (Blue), 0x0000FF00 (Green), 0x00FF0000 (Red) and 0xFF000000 (Alpha). | |||
:8 - RGB888, 32 bits/pixel (stored as a little-Endian int32, swaps to big Endian at runtime on Mac) | |||
::Three 8-bit channels, with bitmasks 0x000000FF (Blue), 0x0000FF00 (Green) and 0x00FF0000 (Red). | |||
:::N.B. The high byte (0xFF000000) is unused, but the convention is to always set it to 0x00. | |||
:9 - S3TC/DXT1, RGB565 compressed 4 times ([https://www.khronos.org/opengl/wiki/S3_Texture_Compression GL_COMPRESSED_RGB_S3TC_DXT1_EXT] OpenGL texture format) | |||
:10 (never used in Vanilla TXMPs) - RGB_Bytes, 24 bits/pixel, stored as 3 consecutive bytes: first Red, then Green, then Blue. | |||
::N.B. Unlike for RGB888 (type 8), the storage is compact, with no unused alpha bit. | |||
:11 (never used in Vanilla TXMPs<ref>Storage format 11 (RGBA_Bytes) was effectively implemented by OniSplit to allow for 32-bit textures with transparency - most importantly experimental lightmaps, see [[Lightmapping_levels|HERE]]. However, it was mislabeled as type 7 (ARGB8888) by OniSplit, Daodan DLL and the Intel Mac build, which resulted in byte swapping and the requirement of authoring PC and Mac versions of TXMPs.</ref>) - RGBA_Bytes, 32 bits/pixel, stored as 4 consecutive bytes: first Red, then Green, then Blue, then Alpha. | |||
:12 (never used in Vanilla TXMPs) - RGBA5551, 16 bits/pixel (stored as a little-Endian int16, swaps to big Endian at runtime on Mac) | |||
::Three 5-bit channels with bitmasks 0x003E (Blue), 0x07C0 (Green) and 0xF800 (Red), 1-bit alpha (0x0001). | |||
:13 (never used in Vanilla TXMPs) - RGBA4444, 16 bits/pixel (stored as a little-Endian int16, swaps to big Endian at runtime on Mac) | |||
::Four 4-bit channels, with bitmasks 0x00F0 (Blue), 0x0F00 (Green), 0xF000 (Red) and 0x000F (Alpha). | |||
:14 (never used in Vanilla TXMPs) - RGB565, 16 bits/pixel (stored as a little-Endian int16, swaps to big Endian at runtime on Mac) | |||
::Two 5-bit channels with bitmasks 0x001F (Blue) and 0xF800 (Red), 6-bit Green channel (0x07E0). | |||
:15 (never used in Vanilla TXMPs) - ABGR1555, 16 bits/pixel (stored as a little-Endian int16, swaps to big Endian at runtime on Mac) | |||
::Three 5-bit channels with bitmasks 0x001F (Red), 0x03E0 (Green) and 0x7C00 (Blue), 1-bit alpha (0x8000). | |||
}} | |||
{{OBDtr| 0x94 | link |FFC8FF| 00 00 00 00 | unused | link to a [[OBD:TXAN|TXAN]] file; used if this texture is animated }} | {{OBDtr| 0x94 | link |FFC8FF| 00 00 00 00 | unused | link to a [[OBD:TXAN|TXAN]] file; used if this texture is animated }} | ||
{{OBDtr| 0x98 | link |FFC800| 00 00 00 00 | unused | link to a TXMP file that contain the environment map }} | {{OBDtr| 0x98 | link |FFC800| 00 00 00 00 | unused | link to a TXMP file that contain the environment map }} | ||
| Line 50: | Line 73: | ||
;Pixel storage order | ;Pixel storage order | ||
: | :Pixels are stored in row-major order, meaning that all the pixels forming a scanline (image row) are grouped together (stored in left-to right order); the rows are stored in bottom-to-top order (see illustration below). | ||
:In the case of the DXT1 storage format, the row-major, left-to-right, bottom-to-top order applies to the 4x4 blocks composing the image, and also inside each 4x4 block for the storage of 2-bit pixels. | |||
:In the case of the I1 format (several pixels per byte), the row-major, left-to-right, bottom-to-top order applies to the 1-bit pixels composing the image. | |||
{|border=0 | {|border=0 | ||
|+Pixel arrangement | |+Pixel arrangement | ||
| Line 61: | Line 85: | ||
| | | | ||
|[[Image:txmp_ex2.gif]] | |[[Image:txmp_ex2.gif]] | ||
|} | |||
<!-- | |||
;Oni's internal storage types | |||
There are 16 types of image storage in Oni: | |||
*The first 9 types are stored as integers (little Endian in PC memory and in TXMP, big Endian in Mac memory) | |||
The | |||
{|border=1 cellspacing=0 cellpadding=3 | |||
!N° | |||
!ID | |||
!Examples for colors | |||
!Notes | |||
|- | |||
|0 | |||
|ARGB4444 | |||
|0x00 0xFC | |||
| | |||
|Treated as 16-bit integer: stored as big-endian in TXMP (first the AAAARRRR byte, then the GGGGBBBB byte), but byte-swapped to little-endian on Mac platforms. | |||
|- | |||
|1 | |||
|RGB555 | |||
|16-bit integer, unused high bit set to 1 | |||
|Red: 0xStored in little-endian order in TXMP, unused high bit is set to 1. #FF0000 | |||
|- | |||
|} | |||
Bits (low-to-high) of storage bytes as in TXMP (little-endian) | |||
---- | |||
;ARGB4444 (format N°0) | |||
*A 16-bit field is used to store 4 color channels (4 bits each, values from 0 to 15). | |||
*Bit masks are 0x000F for Blue, 0x00F0 for Green, 0x0F00 for Red, 0xF000 for Alpha. | |||
*In Mac RAM the two bytes appear in big Endian order (high byte first). | |||
*In PC RAM and in TXMP files the two bytes appear in little Endian order. | |||
{|border=1 cellpadding=3 cellspacing=0 | |||
!<br/>Bits | |||
!Byte 1 (high)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
!Byte 0 (low)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
|- | |||
!Masks||<code>A A A A R R R R</code>||<code>G G G G B B B B</code> | |||
|- | |||
!colspan=3|<br/>Bit values for primary colors (fully opaque) | |||
!Hex view<br/>(Mac RAM) | |||
!(TXMP and <br/>PC RAM) | |||
|- | |||
|Black||<code>1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!F0 00!!00 F0 | |||
|- | |||
|White||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FF FF!!FF FF | |||
|- | |||
|Red||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!FF 00!!00 FF | |||
|- | |||
|Green||<code>1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!F0 F0!!F0 F0 | |||
|- | |||
|Blue||<code>1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!F0 0F!!0F F0 | |||
|- | |||
|Cyan||<code>1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!F0 FF!!FF F0 | |||
|- | |||
|Magenta||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FF 0F!!0F FF | |||
|- | |||
|Yellow||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!FF F0!!F0 FF | |||
|} | |||
---- | |||
;RGB555 (format N°1) | |||
*A 16-bit field is used to store 3 color channels (5 bits each, values from 0 to 31). | |||
*Bit masks are 0x001F for Blue, 0x03E0 for Green, 0x7C00 for Red. | |||
*The high bit (0x8000) is unused, but is always set to 1 by convention. | |||
*In Mac RAM the two bytes appear in big Endian order (high byte first). | |||
*In PC RAM and in TXMP files the two bytes appear in little Endian order. | |||
{|border=1 cellpadding=3 cellspacing=0 | |||
!<br/>Bits | |||
!Byte 1 (high)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
!Byte 0 (low)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
|- | |||
!Masks||<code>X R R R R R G G</code>||<code>G G G B B B B B</code> | |||
|- | |||
!colspan=3|<br/>Bit values for primary colors | |||
!Hex view<br/>(Mac RAM) | |||
!(TXMP and <br/>PC RAM) | |||
|- | |||
|Black||<code>1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!80 00!!00 80 | |||
|- | |||
|White||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FF FF!!FF FF | |||
|- | |||
|Red||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!FC 00!!00 FC | |||
|- | |||
|Green||<code>1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!83 E0!!E0 83 | |||
|- | |||
|Blue||<code>1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!80 1F!!1F 80 | |||
|- | |||
|Cyan||<code>1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!83 FF!!FF 83 | |||
|- | |||
|Magenta||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FC 1F!!1F FC | |||
|- | |||
|Yellow||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!FF E0!!E0 FF | |||
|} | |||
---- | |||
;ARGB1555 (format N°2) | |||
*A 16-bit field is used to store 3 color channels (5 bits each, values from 0 to 31) and one 1-bit channel. | |||
*Bit masks are 0x001F for Blue, 0x03E0 for Green, 0x7C00 for Red, and 0x8000 for Alpha. | |||
*In Mac RAM the two bytes appear in big Endian order (high byte first). | |||
*In PC RAM and in TXMP files the two bytes appear in little Endian order. | |||
{|border=1 cellpadding=3 cellspacing=0 | |||
!<br/>Bits | |||
!Byte 1 (high)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
!Byte 0 (low)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
|- | |||
!Masks||<code>A R R R R R G G</code>||<code>G G G B B B B B</code> | |||
|- | |||
!colspan=3|<br/>Bit values for primary colors (opaque) | |||
!Hex view<br/>(Mac RAM) | |||
!(TXMP and <br/>PC RAM) | |||
|- | |||
|Black||<code>1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!80 00!!00 80 | |||
|- | |||
|White||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FF FF!!FF FF | |||
|- | |||
|Red||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!FC 00!!00 FC | |||
|- | |||
|Green||<code>1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!83 E0!!E0 83 | |||
|- | |||
|Blue||<code>1 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!80 1F!!1F 80 | |||
|- | |||
|Cyan||<code>1 0 0 0 0 0 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!83 FF!!FF 83 | |||
|- | |||
|Magenta||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FC 1F!!1F FC | |||
|- | |||
|Yellow||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!FF E0!!E0 FF | |||
|} | |||
---- | |||
;A4I4 (format N°6) | |||
*An 8-bit field is used to store an intensity and an alpha (4 bits each, values from 0 to 15). | |||
*Bit masks are 0x0F for Intensity, 0xF0 for Alpha. | |||
*Endianness is irrelevant for single-byte storage. | |||
{|border=1 cellpadding=3 cellspacing=0 | |||
!Bits | |||
!<code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
|- | |||
!Masks||<code>A A A A I I I I</code> | |||
|- | |||
!colspan=2|Examples of bit values | |||
!Hex view | |||
|- | |||
|Black, opaque||<code>1 1 1 1 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!F0 | |||
|- | |||
|White, opaque||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FF | |||
|- | |||
|Black, transparent||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!00 | |||
|- | |||
|White, transparent||<code>0 0 0 0 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!0F | |||
|} | |||
---- | |||
;ARGB8888 (format N°7) | |||
*A 32-bit field is used to store 4 color channels (8 bits each, values from 0 to 255). | |||
*Bit masks are 0x000000FF for Blue, 0x0000FF00 for Green, 0x00FF0000 for Red, 0xFF000000 for Alpha. | |||
*In Mac RAM the four bytes appear in big Endian order (high byte first). | |||
*In PC RAM and in TXMP files the four bytes appear in little Endian order. | |||
{|border=1 cellpadding=3 cellspacing=0 | |||
!<br/>Bits | |||
!Byte 3 (highest)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
!Byte 2 (higher)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
!Byte 1 (high)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
!Byte 0 (low)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
|- | |||
!Masks||<code>A A A A A A A A</code>||<code>R R R R R R R R</code>||<code>G G G G G G G G</code>||<code>B B B B B B B B</code> | |||
|- | |||
!colspan=5|<br/>Bit values for primary colors (fully opaque) | |||
!Hex view<br/>(Mac RAM) | |||
!(TXMP and <br/>PC RAM) | |||
|- | |||
|Black||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!FF 00 00 00!!00 00 00 FF | |||
|- | |||
|White||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FF FF FF FF!!FF FF FF FF | |||
|- | |||
|Red||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!FF FF 00 00!!00 00 FF FF | |||
|- | |||
|Green||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!FF 00 FF 00!!00 FF 00 FF | |||
|- | |||
|Blue||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FF 00 00 FF!!FF 00 00 FF | |||
|- | |||
|Cyan||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FF 00 FF FF!!FF FF 00 FF | |||
|- | |||
|Magenta||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FF FF 00 FF!!FF 00 FF FF | |||
|- | |||
|Yellow||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!FF FF FF 00!!00 FF FF FF | |||
|} | |||
---- | |||
;RGB888 (format N°8) | |||
*A 32-bit field is used to store 3 color channels (8 bits each, values from 0 to 255). | |||
*Bit masks are 0x000000FF for Blue, 0x0000FF00 for Green, 0x00FF0000 for Red. | |||
*The high byte (0xFF000000) is unused, but is always set to 00 by convention. | |||
*In Mac RAM the four bytes appear in big Endian order (high byte first). | |||
*In PC RAM and in TXMP files the four bytes appear in little Endian order. | |||
{|border=1 cellpadding=3 cellspacing=0 | |||
!<br/>Bits | |||
!Byte 3 (highest)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
!Byte 2 (higher)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
!Byte 1 (high)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
!Byte 0 (low)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
|- | |||
!Masks||<code>X X X X X X X X</code>||<code>R R R R R R R R</code>||<code>G G G G G G G G</code>||<code>B B B B B B B B</code> | |||
|- | |||
!colspan=5|<br/>Bit values for primary colors | |||
!Hex view<br/>(Mac RAM) | |||
!(TXMP and <br/>PC RAM) | |||
|- | |||
|Black||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!00 00 00 00!!00 00 00 00 | |||
|- | |||
|White||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!00 FF FF FF!!FF FF FF 00 | |||
|- | |||
|Red||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!00 FF 00 00!!00 00 FF 00 | |||
|- | |||
|Green||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!00 00 FF 00!!00 FF 00 00 | |||
|- | |||
|Blue||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!00 00 00 FF!!FF 00 00 00 | |||
|- | |||
|Cyan||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!00 00 FF FF!!FF FF 00 00 | |||
|- | |||
|Magenta||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!00 FF 00 FF!!FF 00 FF 00 | |||
|- | |||
|Yellow||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!00 FF FF 00!!00 FF FF 00 | |||
|} | |||
---- | |||
;RGB_Bytes (format N°10) | |||
*Three consecutive 8-bit fields are used to store 3 color channels (8 bits each, values from 0 to 255). | |||
*Each channel has its own byte, and there is no "unused" byte (the bytes are packed 3 by 3). | |||
*Endianness is irrelevant when storing as a sequence of bytes. | |||
{|border=1 cellpadding=3 cellspacing=0 | |||
!<br/>Bits | |||
!Byte 0 (red)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
!Byte 1 (green)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
!Byte 2 (blue)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
|- | |||
!Masks||<code>R R R R R R R R</code>||<code>G G G G G G G G</code>||<code>B B B B B B B B</code> | |||
|- | |||
!colspan=4|Bit values for primary colors | |||
!Hex view | |||
|- | |||
|Black||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!00 00 00 | |||
|- | |||
|White||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FF FF FF | |||
|- | |||
|Red||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!FF 00 00 | |||
|- | |||
|Green||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!00 FF 00 | |||
|- | |||
|Blue||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!00 00 FF | |||
|- | |||
|Cyan||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!00 FF FF | |||
|- | |||
|Magenta||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FF 00 FF | |||
|- | |||
|Yellow||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code> | |||
!FF FF 00 | |||
|} | |||
---- | |||
;RGBA_Bytes (format N°11) | |||
*Four consecutive 8-bit fields are used to store 4 color channels (8 bits each, values from 0 to 255). | |||
*Each channel has its own byte. Endianness is irrelevant when storing as a sequence of bytes. | |||
{|border=1 cellpadding=3 cellspacing=0 | |||
!<br/>Bits | |||
!Byte 0 (red)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
!Byte 1 (green)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
!Byte 2 (blue)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
!Byte 3 (alpha)<br/><code>7 6 5 4 3 2 1 0</code> | |||
|- | |||
!Masks||<code>R R R R R R R R</code>||<code>G G G G G G G G</code>||<code>B B B B B B B B</code>||<code>A A A A A A A A</code> | |||
|- | |||
!colspan=5|<br/>Bit values for primary colors (fully opaque) | |||
!Hex view | |||
|- | |||
|Black||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!00 00 00 FF | |||
|- | |||
|White||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FF FF FF FF | |||
|- | |||
|Red||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FF 00 00 FF | |||
|- | |||
|Green||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!00 FF 00 FF | |||
|- | |||
|Blue||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!00 00 FF FF | |||
|- | |||
|Cyan||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!00 FF FF FF | |||
|- | |||
|Magenta||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FF 00 FF FF | |||
|- | |||
|Yellow||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code>||<code>0 0 0 0 0 0 0 0</code>||<code>1 1 1 1 1 1 1 1</code> | |||
!FF FF 00 FF | |||
|} | |} | ||
(GL_RGBA4 OpenGL texture format) | |||
(GL_RGB5 OpenGL texture format) | |||
(GL_RGB5_A1 OpenGL texture format) | |||
(GL_RGB OpenGL texture format) RGB888 | |||
--> | |||
==Notes== | |||
<references/> | |||
{{OBD_File_Footer | type=TXMP | prev=TXMB | next=TxtC | name=Texture Map | family=Generic}} | {{OBD_File_Footer | type=TXMP | prev=TXMB | next=TxtC | name=Texture Map | family=Generic}} | ||
{{OBD}} | {{OBD}} | ||
Revision as of 01:28, 9 July 2021
|
|

|
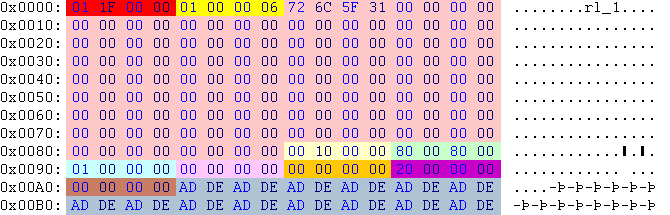
| Offset | Type | Raw Hex | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | res_id | 01 1F 00 00 | 31 | 00031-rl_1.TXMP |
| 0x04 | lev_id | 01 00 00 06 | 3 | level 3 |
| 0x08 | char[128] | rl_1 | name of the texture; unused | |
| 0x88 | int32 | 00 10 00 00 | 0x1000 | options; possible option flags (from left to right):
|
| 0x8C | int16 | 80 00 | 128 | width of the image in pixels |
| 0x8E | int16 | 80 00 | 128 | height of the image in pixels |
| 0x90 | int32 | 01 00 00 00 | 1 | texture format #1 (RGB555); see below for list of available formats.
|
| 0x94 | link | 00 00 00 00 | unused | link to a TXAN file; used if this texture is animated |
| 0x98 | link | 00 00 00 00 | unused | link to a TXMP file that contain the environment map |
| 0x9C | offset | 20 00 00 00 | 00 00 00 20 | at this position starts the texture part in the raw file (Windows only) |
| 0xA0 | offset | 00 00 00 00 | unused | at this position starts the texture part in the separate file (Mac retail/demo and Windows demo only) |
| 0xA4 | char[28] | AD DE | dead | unused |
- Effect options
- "Shield", "Invisibility" and "Daodan shield" options do not affect the texture reading/drawing in any way. The texture data is still RGB555 or whatever format the texture format field says it is. The effect of these flags is that the engine uses vertex shading with a colour that varies with time.
- Animation time
When using animated textures the image to display is selected using the game time and animation speed. For textures that are used by particles the local (particle) time can be used either to replace or offset the game time.
- Pixel storage order
- Pixels are stored in row-major order, meaning that all the pixels forming a scanline (image row) are grouped together (stored in left-to right order); the rows are stored in bottom-to-top order (see illustration below).
- In the case of the DXT1 storage format, the row-major, left-to-right, bottom-to-top order applies to the 4x4 blocks composing the image, and also inside each 4x4 block for the storage of 2-bit pixels.
- In the case of the I1 format (several pixels per byte), the row-major, left-to-right, bottom-to-top order applies to the 1-bit pixels composing the image.
| how it's stored | how you'll see it | |
|---|---|---|

|

|
Notes
- ↑ Storage format 7 was jointly used by OniSplit, Daodan DLL and the Intel Mac build to allow for 32-bit textures with transparency - most importantly experimental lightmaps, see HERE. However, the actual storage format used in this case was RGBA_Bytes (type 11), and type 7 was used by mistake.
- ↑ Storage format 11 (RGBA_Bytes) was effectively implemented by OniSplit to allow for 32-bit textures with transparency - most importantly experimental lightmaps, see HERE. However, it was mislabeled as type 7 (ARGB8888) by OniSplit, Daodan DLL and the Intel Mac build, which resulted in byte swapping and the requirement of authoring PC and Mac versions of TXMPs.
| ONI BINARY DATA |
|---|
| TXMB << Other file types >> TxtC |
| TXMP : Texture Map |
| Generic file |