OBD:TSGA: Difference between revisions
m (wording; linking to OBD:Text encoding) |
m (there there) |
||
| Line 4: | Line 4: | ||
Every TSGA file contains 256 elements of 20 bytes each, thus taking up 5,120 bytes without the header. Together with the 8-byte header and 32-byte padding, each TSGA takes up 5,152 bytes in a .dat (another 20 bytes are taken up in the instance descriptor array). | Every TSGA file contains 256 elements of 20 bytes each, thus taking up 5,120 bytes without the header. Together with the 8-byte header and 32-byte padding, each TSGA takes up 5,152 bytes in a .dat (another 20 bytes are taken up in the instance descriptor array). | ||
For Western languages, a TSFT has only one TSGA which corresponds to an ASCII- | For Western languages, a TSFT has only one TSGA which corresponds to an ASCII-based [[wp:code page|code page]]: | ||
*the first 32 symbols (0 to 31) are non-printable control characters, so these elements are always all | *the first 32 symbols (0 to 31) are non-printable control characters, so these elements are always all zero; | ||
*the next 96 symbols (32 to 127) correspond to standard ASCII | *the next 96 symbols (32 to 127) correspond to standard US-ASCII (except that 127 is usually non-printable); | ||
*the upper half of the table (128 to 255) is | *the upper half of the table (128 to 255) contains additional punctuations and ligatures, Latin characters with diacritics and, in the case of the Russian version, Cyrillic script. | ||
The code page is not the same for all Western Oni versions. | |||
Asian localizations of Oni use their own extended encoding system and glyph data either in place of Oni's (Chinese), or in combination with it (Japanese). | |||
See [[OBD:Text encoding]] for details on the encoding systems, a list of the available characters in each language version, and a review of known issues. | |||
---- | ---- | ||
| Line 35: | Line 39: | ||
The pixels stored in TSFT (packed 4-by-4 as little-Endian unsigned int32s) are treated as a scanline, row major, top to bottom and left to right. The width of a glyph is not always a multiple of 4 pixels, so the scanline can wrap around, i.e. a new row of pixels can start in the middle of a 4-byte element. The start of a glyph, however, is always aligned on a 4-byte element of the TSFT array. The end of a glyph is padded with 0xDEAD. | The pixels stored in TSFT (packed 4-by-4 as little-Endian unsigned int32s) are treated as a scanline, row major, top to bottom and left to right. The width of a glyph is not always a multiple of 4 pixels, so the scanline can wrap around, i.e. a new row of pixels can start in the middle of a 4-byte element. The start of a glyph, however, is always aligned on a 4-byte element of the TSFT array. The end of a glyph is padded with 0xDEAD. | ||
---- | |||
;Difference in the PS2 implementation | |||
{{Table}} | |||
|- ALIGN=CENTER VALIGN=TOP | |||
{{OBDtr| 0x0C | int32 |FFC800| 00 00 00 00 |unused| position of the pixel glyph data in the .raw part of the [[OBD:TSFT|TSFT]] file, in quarter-bytes }} | |||
{{OBDtr| 0x10 | int32 |C800C8| 00 00 00 00 |unused| runtime only? }} | |||
|} | |||
In the PS2 implementation, glyphs are also rectangular grayscale bitmaps, but the storage is much more compact, with only 2 bits per pixel (i.e., 4 pixels per byte), and the scanline is stored continuously for the whole font, without padding/aligning the beginning of a glyph to whole bytes or 4-byte blocks. The scanline is stored in the .raw part of the TSFT file (as opposed to the PC and Mac implementation, which uses a variable array in the .dat). Within a byte, the pixel order is low-to-high (see the TSFT page for an example). | |||
It is not 100% clear why the template checksum is different for PS2, even though the TSGA structure is essentially the same; the field at 0x0C seems to be an (unsigned) int32 in both cases. The runtime field at 0x10 is also an unsigned int32, rather than a bunch of flags. | |||
Revision as of 16:39, 21 November 2022
|
|

|
Every TSGA file contains 256 elements of 20 bytes each, thus taking up 5,120 bytes without the header. Together with the 8-byte header and 32-byte padding, each TSGA takes up 5,152 bytes in a .dat (another 20 bytes are taken up in the instance descriptor array).
For Western languages, a TSFT has only one TSGA which corresponds to an ASCII-based code page:
- the first 32 symbols (0 to 31) are non-printable control characters, so these elements are always all zero;
- the next 96 symbols (32 to 127) correspond to standard US-ASCII (except that 127 is usually non-printable);
- the upper half of the table (128 to 255) contains additional punctuations and ligatures, Latin characters with diacritics and, in the case of the Russian version, Cyrillic script.
The code page is not the same for all Western Oni versions.
Asian localizations of Oni use their own extended encoding system and glyph data either in place of Oni's (Chinese), or in combination with it (Japanese).
See OBD:Text encoding for details on the encoding systems, a list of the available characters in each language version, and a review of known issues.
| Offset | Type | Raw Hex | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
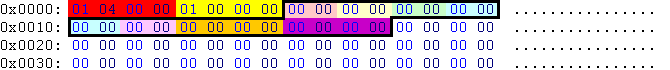
| 0x00 | res_id | 01 04 00 00 | 4 | 00004-.TSGA |
| 0x04 | lev_id | 01 00 00 00 | 0 | level 0 |
| First element (black outline) | ||||
| 0x00 | int16 | 00 00 | unused | character code |
| 0x02 | int16 | 00 00 | unused | width |
| 0x04 | int16 | 00 00 | unused | bitmap width |
| 0x06 | int16 | 00 00 | unused | bitmap height |
| 0x08 | int16 | 00 00 | unused | bitmap x origin |
| 0x0A | int16 | 00 00 | unused | bitmap y origin |
| 0x0C | int32 | 00 00 00 00 | unused | start element in the TSFT file |
| 0x10 | int32 | 00 00 00 00 | unused | runtime only |
A glyph is basically a grayscale bitmap which is (width * height) pixels in size. Each pixel is stored in one byte in the TSFT file (fonts are antialiased so shades of gray are needed rather than storing each pixel in one bit; although for the smallest font size there is no antialiasing in use and the 8-bit pixels are either fully black or fully white).
The pixels stored in TSFT (packed 4-by-4 as little-Endian unsigned int32s) are treated as a scanline, row major, top to bottom and left to right. The width of a glyph is not always a multiple of 4 pixels, so the scanline can wrap around, i.e. a new row of pixels can start in the middle of a 4-byte element. The start of a glyph, however, is always aligned on a 4-byte element of the TSFT array. The end of a glyph is padded with 0xDEAD.
- Difference in the PS2 implementation
| 0x0C | int32 | 00 00 00 00 | unused | position of the pixel glyph data in the .raw part of the TSFT file, in quarter-bytes |
| 0x10 | int32 | 00 00 00 00 | unused | runtime only? |
In the PS2 implementation, glyphs are also rectangular grayscale bitmaps, but the storage is much more compact, with only 2 bits per pixel (i.e., 4 pixels per byte), and the scanline is stored continuously for the whole font, without padding/aligning the beginning of a glyph to whole bytes or 4-byte blocks. The scanline is stored in the .raw part of the TSFT file (as opposed to the PC and Mac implementation, which uses a variable array in the .dat). Within a byte, the pixel order is low-to-high (see the TSFT page for an example).
It is not 100% clear why the template checksum is different for PS2, even though the TSGA structure is essentially the same; the field at 0x0C seems to be an (unsigned) int32 in both cases. The runtime field at 0x10 is also an unsigned int32, rather than a bunch of flags.
| ONI BINARY DATA |
|---|
| TSFT << Other file types >> TStr |
| TSGA : Glyph Array |
| Global file |