OBD:BINA/OBJC: Difference between revisions
< OBD:BINA
(headers, better intro) |
m (→File description: why did I break this markup with my previous edit?) |
||
| Line 6: | Line 6: | ||
==File description== | ==File description== | ||
;Example file | ;Example file | ||
:OBD:BINA/OBJC/PWRU|CJBOPowerUp.BINA from level 3 | :[[OBD:BINA/OBJC/PWRU|CJBOPowerUp.BINA]] from level 3 | ||
;Offsets | ;Offsets | ||
:Offsets are given with respect to the start of the raw file's data part. | :Offsets are given with respect to the start of the raw file's data part. | ||
Revision as of 20:20, 26 August 2016
|
|

|
Introduction
"OBJC" is short for "Objects", which refers to lists of files which are stored in the separate file when available (Mac and Windows demo) or in the raw file otherwise (Windows). OBJC is registered as a tag (and is also a sub-tag of BINA), but it is really a wrapper for other tags. OBJCs are lists composed of a standard wrapper and then elements of type-specific data which has its own tag. Objects listed in OBJCs could be edited in-game by the developers using the GUI which was discovered by fans in the German Big Blue Box version of Oni. The editing interface is pictured on the pages of the types which the interface could edit.
File description
- Example file
- CJBOPowerUp.BINA from level 3
- Offsets
- Offsets are given with respect to the start of the raw file's data part.
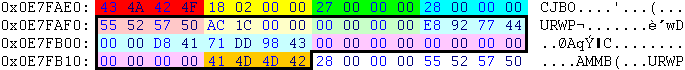
| Offset | Type | Raw Hex | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | 4CC | 43 4A 42 4F | OBJC | objects |
| 0x04 | int32 | 18 02 00 00 | 536 | size to end of object list from 0x08, in bytes |
| 0x08 | int32 | 27 00 00 00 | 39 | object format version |
| 0x0C | int32 | 28 00 00 00 | 40 | size of next object (black outline) |
| 0x10 - 0x37 : first object (40 bytes) | ||||
| 0x38 | int32 | 28 00 00 00 | 40 | size of next object |
| 0x3C - ... : second object (40 bytes), etc | ||||
- General layout
- The list's header (first 16 bytes) and layout is common to all 16 OBJC types (see below).
- The size of the whole list is announced at 0x04 (int32), followed by the list.
- Unlike ONIE and TMBD (which are arrays), OBJC announces the size of every object (int32).
- After the last object, the end of the list is signaled by a null next object size.
- Object header
- All objects start with the following header:
| Offset | Type | Raw Hex | Value | Description |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 0x00 | char[4] | 52 52 57 50 | PWRU | object type |
| 0x04 | int32 | AC 1C 00 00 | 7340 | object ID |
| 0x08 | 00 00 00 00 | 0x00 | object flags; used values:
| |
| 0x0C | float | E8 92 77 44 | 990.254 | x-position |
| 0x10 | float | 00 00 D8 41 | 27.000000 | y-position |
| 0x14 | float | 71 DD 98 43 | 305.73 | z-position |
| 0x18 | float | 00 00 00 00 | 0.000000 | rotation on the x-axis in degrees |
| 0x1C | float | 00 00 00 00 | 0.000000 | rotation on the y-axis in degrees |
| 0x20 | float | 00 00 00 00 | 0.000000 | rotation on the z-axis in degrees |
OBJC types
A given list can only hold objects of one type, which can be:
|
| ONI BINARY DATA |
|---|
| AKVA << Other file types >> CBPI |
| BINA : Binary data |
| TMBD << Other BINA >> ONIE |
| OBJC : Objects |
| [[OBD:File types/{{{family}}}|{{{family}}} file]] |